Lean manufacturing tools and techniques aim to reduce waste potential while making manufacturing processes as efficient as possible. Utilizing the most useful tools and techniques is key to facilitating process optimization.

Muda, Mura, and Muri – The Lean Manufacturing Waste Trifecta
The concept of “lean” ties very closely to principles implemented by Toyota, in their Toyota Production System, as a means of addressing three core challenges in a manufacturing environment: Muda, Mura, and Muri.
Each of these has a different meaning, but all of them detract from the effectiveness and value creation within the manufacturing process. Specifically, these three terms have the following connotations:
- Muda – Waste in any form, whether it be time, resources, or efficiency
- Mura – Unevenness, or irregularity (generally in the process management sphere) that leads to waste
- Muri – Overburden, overload, or being unreasonable; to expect more than people, tools, or resources are capable of doing
How do these concepts interconnect, and how do they relate to lean manufacturing tools and techniques?
Simply put, Muda (waste) is the primary challenge that lean manufacturing tries to eliminate since it can lead to a domino effect within the production process. Subsequently, addressing Mura (unevenness) in the manufacturing process, allows you to automatically eliminate waste by distributing work across teams and resources more evenly.
Muri (overburden) can be removed by closely monitoring and assessing capacity across all manufacturing areas, including workstations, machines, and employees. From there, businesses can focus on creating optimal balance across the organization through planning and effective resource allocation. It should be noted that adjusting any of the three challenges can affect the others as well.
The idea of lean manufacturing has taken different forms over the years, with some companies developing their own variations of the concept. Let’s explore some of the most prominent methodologies that have been successfully utilized across the industry.
Kaizen
Kaizen, from the Japanese phrase meaning “good change” or “continuous improvement,” is a strategy wherein employees work proactively to create consistent improvements but in minuscule increments.
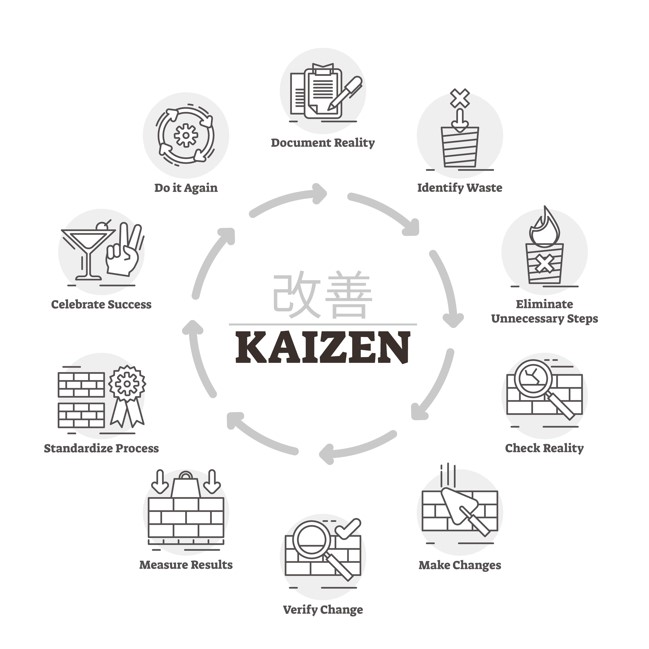
Also known as rapid improvement processes, Kaizen is often considered the building block of most other lean production systems. Additionally, its focus is on:
- Eliminating waste
- Improving overall productivity
- Achieving sustainable continuous improvement in specific processes
The main strength of this lean technique lies in its ability to implement cultural changes throughout the company. Since every employee is equally involved in constant improvement, it becomes an integral part of the company’s makeup.
This method also teaches employees to use the “five whys” value stream mapping and other analytical techniques. With this knowledge, they can identify waste and pinpoint opportunities to implement any necessary changes in processes.
Using Kaizen to replace scheduled checks to eliminate waste and find problems is beneficial as issues generally get eliminated sooner. There are few lean manufacturing and work automation techniques that are more effective than Kaizen since it can seamlessly integrate with your company’s daily operations.
Rapid continual improvement processes usually require a business to actively foster a culture where employees feel empowered to identify and solve problems themselves. This is why most organizations that use Kaizen-type improvement methods have established processes and ground rules that are clearly communicated and reinforced through employee training.
By using constant analysis to remove Mura and preventing parts of the workflow from becoming overburdened and others from creating waste, this method aims to create a perfect balance.
The 5S System
The 5S System is one of the most diverse lean manufacturing techniques, consisting of five separate, interlocking components. The five parts of this process are as follows:
- Seiri (Sort) – Decide which items in the factory or workflow are important and which aren’t. Eliminate non-essential elements. By getting rid of unnecessary items you can free up valuable space within your business and improve the overall efficiency of the workspace. This step helps to identify tools, materials, and resources that aren’t used often, which can clear up clutter.
- Seiton (Straighten) – Ensure that every item in the factory or workflow has a home. Everything employees need should be easy to find. This component can include labeling, creating specific storage locations, or even implementing certain visual cues to help employees locate items they need – quickly and efficiently.
- Seiso (Shine) – Keep things clean, both physically and digitally, to make problems and waste easier to identify. Regular cleaning routines or scheduled maintenance (for digital components) should be established to keep the workspace tidy and promote an environment of productivity.
- Seiketsu (Standardize) – Create well-defined standards, both for the factory and for work processes. By developing consistent methods and procedures for carrying out tasks, businesses can reduce the chances of variability and increase the reliability of their operations.
- Shitsuke (Sustain) – Create a culture of maintaining standards over the long term and consistently paring down unnecessary processes. However, sustaining the improvements that have been made requires ongoing commitment and discipline. This can involve regular training, audits, and reviews to ensure the standards are implemented and continuously upheld.
The 5S system is an excellent lean manufacturing technique for eliminating unevenness. It allows you to cut down on both waste and overburden by streamlining every process to achieve maximum efficiency.
Utilizing this method in your business can lead to significant improvements in employee morale, safety, efficiency, and productivity. This is the necessary foundation for continuous advancement, making it an important method to consider.
Six Big Losses
A major lean technique used throughout the world, the “Six Big Losses” refers to the six most common causes of waste on the production line or even in a workflow. Specifically, these six things are:
- Breakdowns – Machine breakdowns and breakdowns in system processes. These can lead to downtime and disrupt the flow of the production process, which often requires immediate attention to return operations back to normal.
- Setup and Adjustment – Time spent on setting up or adjusting machinery or workflow processes, including calibration, tool changes, and system reconfiguration. If this time isn’t managed efficiently, it can reduce the efficiency of production.
- Idling or Short Stops – Idling or pauses caused in work due to obstructions, blockages, and other minor problems. These interruptions, although they may seem insignificant on an individual basis, can add up and result in subsequent delays over time.
- Speed Inefficiency – When operators or machines become ineffective, taking excessive amounts of time to accomplish the same tasks. This can be due to a multitude of reasons, like suboptimal machine performance, inadequate training, or ergonomic issues that can slow the production rate.
- Defects – Damages to products, which need to be corrected. Defects often need rework or repair, eating into additional resources and time. This can lead to even more delays further down the production line.
- Rejects – Products rejected from the manufacturing line due to damages, defects, or other inconsistencies. Rejects represent a complete loss of labor, resources, and time that was invested in the production of these faulty items. As a result, the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of operations are negatively impacted.
Monitoring the six big losses is a useful lean technique that helps to cut down on waste, overburden, and unbalance.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Overall Equipment Effectiveness, or OEE, is a useful framework for measuring loss of productivity within any given process. It provides businesses with a comprehensive assessment of how effectively operations are used compared to their full potential. Typically it focuses on three different categories of waste, namely:
- Downtime: This refers to any period when equipment is not in operation. This could be due to breakdowns, maintenance, or other stoppages that are unavoidable.
- Slow Cycles: Slow cycles are usually a result of less-than-optimal machine performance, operator inefficiencies, or process bottlenecks. Identifying and addressing the root cause of these slow cycles can help to optimize the speed and efficiency of the production line.
- Rejects: These are any products that fail to meet quality control standards and are therefore rejected, wasting resources and time. However, by implementing quality control measures, businesses can reduce the number of incidents and rejects to boost product quality.
By providing a baseline for what is an acceptable overall equipment effectiveness level, companies and manufacturers can modify existing workflows and processes to achieve better OEE.

This lean manufacturing tool focuses on eliminating waste, thereby also creating better balance and reducing the burden placed on certain parts of the manufacturing process.
Maintaining your equipment in an optimal condition will also increase the profitability of the enterprise as a whole by eliminating time and resource waste. By shifting these elements to where they’re truly needed, the company can produce more products of the type and specification currently required to fulfill orders.
Kanban
Kanban is a Japanese word meaning “billboard” or “signboard.” Historically, employees would use a physical “signal” card to note that the company needed to acquire something such as supplies needed for a process, or a new part for a machine.
That card would then be taken (generally by a runner) to the person in charge of acquiring that particular item. The sole requirement of the system was that the signal card may only be filled in when that item was truly needed.
Today, this process is mainly digital and doesn’t use any runners. Instead, employees fill out a digital signal card, which instantly travels to the appropriate member of the acquisitions team.
Also, it’s important to recognize that the Kanban system is now used across many different kinds of workflows and processes. It’s no longer relegated to just order processing for supplies. Instead, a basic introduction to lean manufacturing tells us that this multi-faceted approach is ideal.

So, how does Kanban benefit lean manufacturing processes? By streamlining any workflow or process so the business operates more efficiently and effectively, Muda, (waste) in multiple forms can be eliminated
Additionally, if we use supply acquisition as an example, Muri (overburden) is reduced through better resource allocation and inventorying only those items that are required to be on hand at all times. And Mura (unevenness) can be more closely monitored and adjusted through a more agile and adaptable approach to the day-to-day. Business Process Management Platforms
So how does a company get to implementing lean manufacturing practices, or improve upon practices that have already been in place for a long period of time?
How Lean Manufacturing Impacts The Manufacturing Process
Undoubtedly, you or your organization have been involved in or at least apprised of the massive shift to “digital” in today’s business environments. Manufacturing, in particular, is going through massive change under the moniker of Industry 4.0. Robotics and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are in the limelight and offer significant value to certain parts of a manufacturer’s infrastructure.
But what about going beyond equipment and warehouse automation? The workforce is as important to achieving “lean” manufacturing as is managing the technical and physical aspects of manufacturing.
The good news is that new technologies are also allowing for improvements in how work is managed at scale. This includes automation of tasks where appropriate, full visibility of work across teams, better quality control, and more secure management of all work activities – especially those where auditability is critical.
This is where workflow automation and business process management platforms like HighGear come into play.
Why Choose HighGear
HighGear’s workflow solutions have been purpose-built for managing work (particularly in a manufacturing environment) in an agile and adaptable way – all without writing a single line of code.
As a result, HighGear’s solutions like no-code development allow all team members to seamlessly orchestrate their work regardless of their location. The platform provides managers and decision-makers real-time visibility into how the components of any workflow or process are operating.
From a lean manufacturing perspective, it is this detailed visibility, permissions-enabled activity and extensive work orchestration capability that provide real value.
With good workflow automation, eliminating waste, creating balance, and achieving evenness is feasible beyond the shop floor. Whether it’s first call to first article or building robust quality or quoting processes, getting even “leaner” has never been more achievable. So, be sure to book a demo today.
