
Achieving maximum operational efficiency, efficacy and excellence is a top priority for most business leaders. That, however, requires harmony between all business processes, which many believe is unattainable.
This simply isn’t true. While challenging, achieving full operational efficacy is possible through the use of the right tools and implementation of best practices or execution of continuous improvement approaches. Enter the formal practice of business process management (BPM).
What Is Business Process Management?
In simple terms, business process management is an approach to improving and optimizing existing processes within an organization. The BPM definition is, however, much broader than that.
As defined by Gartner, business process management is a discipline that incorporates various methods to discover, model, analyze, measure, improve, and optimize business processes.
Due to its definition, many confuse BPM with task management or project management. The primary difference is that business process management has a much broader scope.
Task management, for example, focuses on individual tasks, whereas BPM concentrates on end-to-end processes. Often, task management is a sub-component of BPM. The same goes for project management, which refers to one-time business operations. Instead, BPM focuses on repetitive and ongoing processes.
Business process management is, therefore, continuously playing an essential role in a company’s entire business strategy, and aiming to generate greater business value.
Due to the complexity of managing tasks and processes, companies incorporate business process management software to automate business processes and task distribution. This includes a view on managing work at scale. Depending on how one looks at it, workflow management either encapsulates many processes or may be a subset of one discreet business process.
Why Is Business Process Management Important?
Imagine what can happen when you leave a business project or activity unmanaged. Time delays? Errors? Financial loss? What about the quality of the end product in a manufacturing environment?
The reality is that even the smallest business process can influence your business outcomes. More complex business processes, however, can lead to total mayhem when not managed efficiently.
Poor process and workflow management can severely hurt your organization, leading to:
- poor employee and customer experiences,
- lower productivity and business efficiency,
- increased operational errors,
- wasted time.
Deploying the right business process management tools can prevent these negative outcomes, improving organizational efficiency and helping a company achieve its business objectives – better customer and employee experiences as well as improved financial outcomes and market competitiveness.

What Are the Types of Business Process Management Approaches?
As stated, the ultimate goal of business process management is to improve and optimize existing processes. However, since there are multiple processes in any organization, BPM solutions can be categorized by the specific purpose they serve.
We can distinguish three main business process management types – human-centric, system-centric, and document-centric.
Human-Centric BPM
Human-centric BPM centers around processes that include human involvement. Typically, these are processes that aren’t highly automated, are performed by individuals, and involve approval components.
Examples of human-centric processes include customer service, employee onboarding, filling reports, etc.
System-Centric BPM
Contrary to human-centric BPM, system-centric (or integration-centric) BPM focuses on the use of software systems to manage large components of a process. Or it may involve fully automating a number of processes and ensuring that the systems used are integrated. These tasks and work activities represented don’t rely much on human involvement and depend on existing platforms such as a CRM or HRM.
Document-Centric BPM
Document-centric BPM refers to managing processes that involve a specific type of documents, such as a contract or agreement. Business process management tools that help with routing, formatting, verifying, and signing documents apply here and are used to speed up the entire process.
What Are the 5 Stages In the BPM Lifecycle?
Business process management requires careful planning for it to be successful. To ensure BPM activities are implemented correctly, organizations refer to the BPM lifecycle when creating their process management strategy.
BPM professionals leverage five stages in process management – designing, modeling, monitoring, executing, and optimizing.
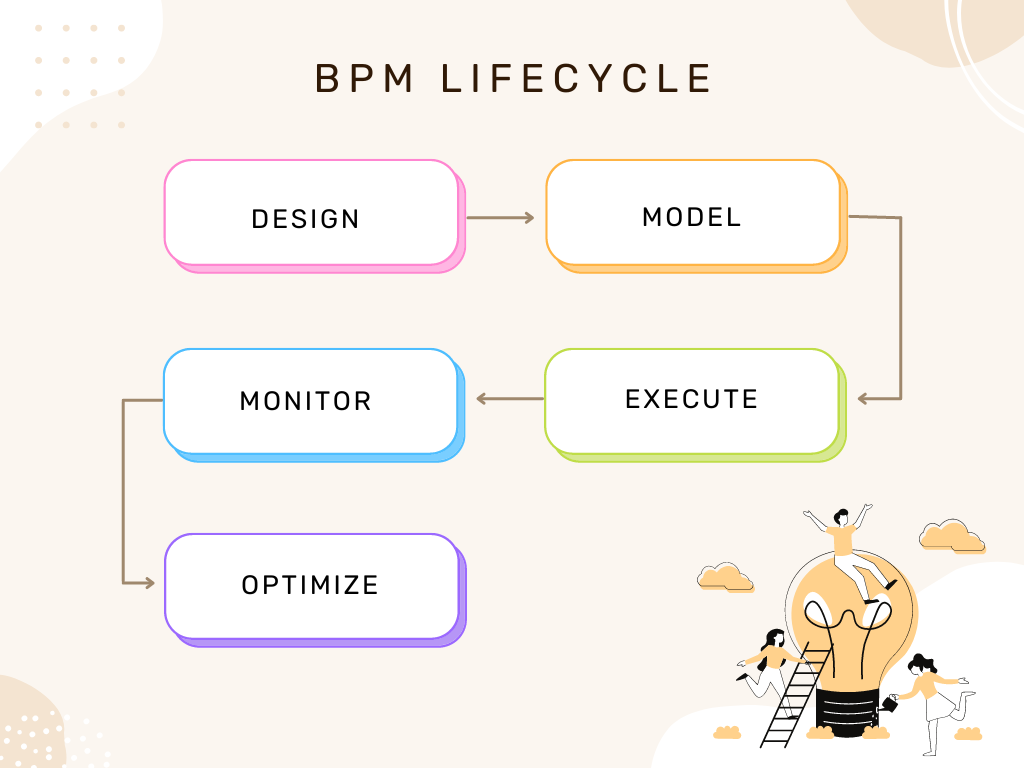
1. Design
The first step in a BPM lifecycle is to analyze and review the company’s current business rules and processes. The goal here is to identify which processes require improvements and outline the objectives and milestones within the process. Note that it’s not important to try to map every process in any given area all at once. Iterative approaches often work best.
It is, however, essential to define process steps and decide on metrics to measure them. It’s also vital to identify individual tasks performed within a workflow and/or process and to understand the task’s relationship to an overall schematic. By starting on a smaller scale with a team or department, process improvement won’t seem so daunting. Incremental gains will start to take shape and influence the assessment of other, more far-reaching processes as things start taking shape..
2. Model
The second step is to design a step-by-step visual representation or “model” of the process. This should be based on the outline created during the design process step and include specific details, such as timelines, task descriptions, and outcome scenarios.
3. Execute
The next stage is process execution. It typically divides into two steps:
- Business process testing;
- Rolling out the process improvement.
The first step here includes introducing the new business process approach to a limited group and gaining feedback. If the feedback is positive, the business can start rolling out the new process to a broader audience. As part of step three, activating a new or improved process may involve the use of a BPM software tool or platform to effectively manage the activity and strategy.
In today’s, digitally-focused environments, process improvement often involves the use of software tools. Many platforms are designed to automate repetitive process tasks allowing for even the most highly complex activities to be managed and securely controlled in one place.
Buyer’s guides, like the one found here, may help support the analysis of software tools to be included in improving any given process.
4. Monitor
Once implemented, it is important to measure how the improved process is performing. The process metrics developed in the design stage can serve as a baseline for the creation of dashboards and other types of reports that will help team members and managers alike.
5. Optimize
The final step is process optimization. During this stage, businesses analyze process performance data and apply the necessary improvements for it to perform more efficiently. In a “continuous improvement” environment, making updates and changes to processes is ongoing. Refinement occurs until it is determined that a process can no longer be optimized.
Also, process improvement and optimization are not typically one-off activities. If an organization wants BPM to routinely produce better business outcomes, it needs to measure and improve an organization’s activities continuously. .
Where Can BPM and Related Software Tools Be Applied?
Business process management can significantly improve performance across an entire organization. Good examples of where BPM systems can perform exceptionally well include:
Human Resources
HR teams can incorporate BPM approaches to streamline workflow and document management. Human Resource departments can also use dedicated BPM software to create a more structured and organized environment for processing forms, invoices, and other documents.
Beyond document control, a business process management system can automate employee onboarding and offboarding, as well as manage performance evaluations and vacation requests. It can also help measure work time and productivity, as well as allow for workforce resource allocation.
Finance
Financial teams can use BPM tools to create and standardize purchase orders, vendor management, expense control, and other financial documents to optimize a finance department’s processes. It’s also possible to customize workflows for different scenarios, such as federal tax management and capital expenditure processing. More efficient process management here can help organizations oversee a vast array of finance activities, ultimately delivering more cost-effective ways to manage in-depth financial activities
Content Distribution
Business process management systems offer a fantastic opportunity for media firms to automate content preparation and delivery processes. Using BPM software, businesses can automate content creation and distribution, as well as create automated tasks regarding content interaction, traffic, and orders.
Sales
Sales quoting and estimating processes can be complex and unwieldy – especially in industries such as manufacturing. This is where business automation technologies can significantly speed things up and enhance the customer experience. . By automating such processes, teams can eliminate human error and ensure more timely and accurate quotes and product samples get processed, contributing to a higher number of sales and translating to increased revenue.
How Can Implementing Business Process Management Help Your Organization?
Business process management offers multiple benefits to business organizations. Some of them have already been mentioned; here’s a more detailed overview of BPM benefits.
Improved Work and Cost-Efficiency
Even the tiniest disruption in business processes can severely affect the organization’s efficiency, both in work and costs. Business process management helps identify and eliminate any process gaps and bottlenecks that might reduce costs over time.
Then, by optimizing and improving these processes, a business can gain more control over its operations, resulting in improved efficiency and further cost savings. BPM also helps allocate and track resources, reducing waste and increasing profits.
Enhanced Business Agility
In the age of everchanging market conditions, all organizations require continuous improvement to stay ahead of the competition. That cannot be achieved, however, without continuously optimized business processes.
This is where business process management comes in. It allows organizations to implement changes, alter workflows, and customize processes for them to be more responsive to ongoing market changes. In other words, BPM improves business agility, which translates into enhanced efficiency and higher revenue.
Better Experience for Your Employees and Customers
Improved business process management can create a better experience for employees and customers. And going one step further, by putting automation into place, improved processes can also allow companies to eliminate repetitive tasks, make information more accessible, and remove distractions and unnecessary paperwork, significantly improving workflows and employee efficiency.
That enhanced efficiency translates into better work outcomes, increasing customer satisfaction in the process. An effective BPM program can also help with employee onboarding, allowing businesses to attract talent into their ranks and increase engagement. Automating this, too, can dramatically improve the employee experience throughout their time with a company, from just getting started to being a lifelong and dedicated contributor.
More Scalable Business Processes
Automated workflows and processes are vital when expanding a business. They significantly improve scalability, bringing clarity to roles and ensuring consistency along throughout a department, office, or company at an enterprise level. BPM technologies also allow organizations to monitor real-time data, allowing process managers to be more informed and current in their decision-making.
Greater Transparency and Seamless Compliance
When using dedicated process management software, businesses can quickly define task owners, enhancing transparency and accountability in the workplace. BPM software can also improve communication between teams.
Besides transparency within the organization, BPM tools also ensure the company complies with internal and external standards, staying up to date with regulations and other performance requirements. . Business process management also promotes security measures across the organization. Every single process is well-documented, which encourages employees to safeguard data and resources.
What Is Business Process Automation?
Throughout this guide, we’ve mentioned that process automation is a vital part of improving one’s business process management. However, while BPM and BPA (business process automation) are closely related, some might say even complementary, they are not the same.
BPA, as stated in its name, refers to automating business processes. BPM, on the other hand, means managing these processes through automation or without it. Simply put, every BPA system is considered BPM, but not all BPM can be considered BPA.
Which processes involve automation? In general, processes that can benefit from automation are usually those started by a triggering event, such as:
- completing HR forms and requests,
- filing an IT support ticket,
- requesting capital expense or budget allowances,
- and completing requests for quotes.
What Are the Types of BPM Technologies?
Although BPM may not always involve automation, the modern-day business environment enforces process improvement through automation. For this purpose, organizations take advantage of business process management software (BPMS).
Such systems typically include several tools and capabilities, including the following:
- process mining tools that enable discovery, representation, and analysis of the task involved in business processes;
- workflow engines that help automate workflow processes;
- business rules engines (BREs) for easily identify key activities and dependencies across workflows;
- simulation and testing tools that allow entrepreneurs to observe how processes behave.
It’s also important to note that there are several types of BPMS, with the three primary ones being iBPMS, LCNC, and RPA:
- iBPMS translates to an intelligent business process system that takes advantage of real-time analytics, machine learning, and complex event monitoring to make process automation more data-driven and dynamic.
- LCNC means low-code/no-code technology. Such BPM tools allow businesses to automate processes without depending on professional coders. HighGear is an example of a no-code workflow platform.
- RPA is an abbreviation for robotic process automation. RPA tools were introduced to automate manual and repetitive tasks. This kind of software mimics the way human employees click and type when doing their tasks, automating these smaller processes to help optimize the more significant and complex processes.
FAQs
What is business process management?
Business process management (BPM) is a discipline that uses various methods and tools to design, model, execute, monitor, and optimize business processes. A business process coordinates the behavior of employees and customers, systems, and information to produce business outcomes that support organizational strategy.
What are the challenges of business process management?
Implementing BPM solutions in a business is a complex process. It is, however, a necessary change one has to incorporate to achieve operational optimization. Due to the complexity of these changes, though, organizations need to prepare to face multiple challenges.
The most common reasons for BPM failures are:
- unclearly stated business objectives and business process change goals;
- lack of real-time process monitoring and data collection;
- inadequate communication between teams.
All of these can be avoided by using the right BPM software.
When are BPM methodologies applicable?
BPM enables businesses to optimize and improve numerous processes. Among the processes that can benefit the most from changes in a BPM process, we can include:
- complex processes that require advanced coordination between numerous teams, business units, and departments;
- business processes requiring fast turnaround;
- dynamic processes requiring regulatory compliance, e.g., changes in finance, privacy, or customer service;
- complex processes involving a triggering event.
What are the benefits of process management?
Taking advantage of automated BPM solutions provides numerous benefits. The right software will allow you to:
- run tasks, projects, and processes more efficiently;
- have more control over business processes;
- improve and optimize complex processes;
- help your business undergo a digital transformation;
- monitor how BPM processes work across the organization;
- realize bigger and more ambitious business goals.
Is BPM expensive?
That depends on the size of your business, the number of processes, and the complexity of your BPM project. When using HighGear, you can pay as low as $63 per month. However, as said, the exact pricing will depend on an organization’s requirements and related platform features.
Improve Your Business Processes with HighGear
If you weren’t sure whether you needed to implement a business process management system before reading this guide, we are confident you now know that it’s not a matter of if but how to incorporate BPM.
The answer is HighGear. Our business process management platform will provide you with everything you need to automate and streamline workflow within your organization to achieve operational efficacy and excellence.
Our platform is entirely no-code, meaning you don’t need professional coders to optimize your processes. It’s a simple-to-use solution that will help you create forms, automate workflows, assign tasks, and review reports.
Schedule a demo or a consultation today, and stay ahead of your competition. Unlock the full potential of your business with HighGear with the most elegant and efficient BPM solution available.
